How to Validate Your Product Idea Before Wasting Your Time and Money
What is product idea validation and why you need to do it?
Step 0: Write down the problem hypothesis as the first step of the idea validation process
Step 1: Start from Researching for your competitors
Step 2: Check search volume and Google Trends
Step 3: Talk your idea to the relevant people
Step 4: Find the value proposition for your product ideas
Step 5: Launch an idea validation landing page
Step 6: Run customer validation survey
Step 7: Paying customers are the best idea validation
Step 8: Run Adwords campaign and FB ads to drive traffic
Step 9: Crowdfunding as a way to validate a product idea
Step 10: Build an MVP
Step 11: Participate in conferences with StartUp Alleys
Great ideas are worthless without execution. But how does one understand if the concept is promising and worth trying? Months and years can pass from the moment when the idea came to the entrepreneur's mind to the day it brings money. Some people get stuck at an early stage of the idea implementation because of their doubts about how to start a business. Others are demotivated by the feedback they received from experts and industry gurus. Many entrepreneurs also waste time and money for marketing, and then eventually come to the conclusion that customers don't need the product or aren't ready to pay for it so far. In this blog post, you will find the best possible way to validate a business idea with a minimum amount of time and money.
What is product idea validation and why you need to do it?
Product idea validation is a step-by-step process. It is designed to provide entrepreneurs with reasonable certainty that their business will have a viable and paying audience within a few days or weeks. This is much better than wasting months/years and thousands of dollars creating a product or service nobody will pay for.
So, if you want to know how to validate a business idea, check out the steps below.
Step 0: Write down the problem hypothesis as the first step of the idea validation process
A lot of people typically start with the solution first. That is not the best place to begin. What you need to do is to take a step back and think about your target audience. What problems does your product or service resolve for the customer? Think about the goal or job your prospective buyer is trying to accomplish. For example: “I believe Dr. Robbins has a problem dealing with paper patient records.” Or: “I believe a photographer Brandon is trying to achieve consistent color appearance across all of his devices because he wants to be able to judge if the printed image reflects what he saw on his camera and monitor.”
Step 1: Start from Researching for your competitors
If you are not creating a whole new market, your idea already has competitors. To understand its viability, look at solutions available on your target market.
Tools to use
There are several tools to analyze competitors.
-
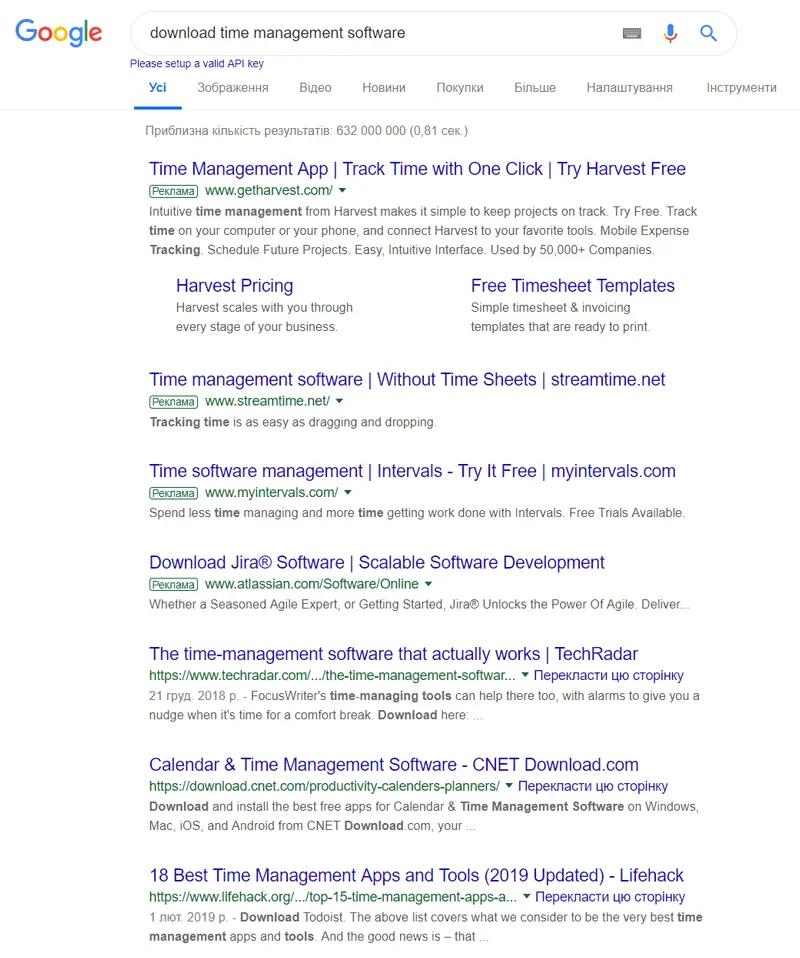
Google
One of the easiest startup validation tools is Google. Prepare a list of keywords related to your product or service and search for these terms on Google. If you want to develop time management software, for example, and you search for this term, you will see who is ranking in the top spots.
-
Review platforms
See what people are saying about the products or services of your competitors on Capterra, G2Crowd, TrustPilot, etc. What do they love and hate about these products? What features are missing? Keep note of these reviews because your ultimate goal is to build a better version of what’s already on the market.
image source: G2Crowd
-
Use # on Instagram and Twitter
In addition to browsing through the official social media pages of competitors, it is also important to analyze references to them in social networks. This will help you track the posts of competitors; analyze your target audience (you will find out if customers are satisfied or dissatisfied with the product of your opponent); identify market participants who actively support your competitors to contact them and tell about your brand; and more.
You may also like our blog post “How to Handle Market Research to Find New Opportunities for Your Business.“
Step 2: Check search volume and Google Trends
Validate your product idea by checking search volume and trends.
Tools to use
-
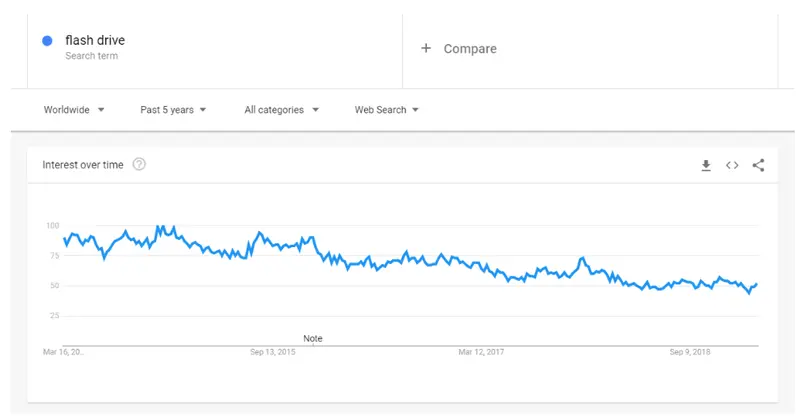
Google Trends
Think of all the possible ways that people might be searching for your products or services. Test your business ideas with this simple tool that shows the development of interest to the given keywords. For example, you put in a keyword, and Google Trends shows the dynamics of search activity, related keywords, and a lot of other useful information.
Obviously, you should not release a product in a stagnant market. For example, over the past five years, requests for the word “flash drive” have begun to fall - most likely, people no longer need flash drives.
-
Ubersuggest
With the help of this tool, you’ll find out how many “exact match” searches happen for your business idea on average per month.

Step 3: Talk your idea to the relevant people
Test your idea by talking about it to as many people as you can. With their help, you will get valuable feedback and refine your idea. Ask people about the problem they have and ask for the best possible solution. There are several ways you can ask for feedback when validating product ideas:
-
Face-to-face interviews
If you know someone who fits into your customer segment, invite them to short face-to-face interviews.
-
Online communities
Think about where your potential customers spend time online and go there. Look for various industry-related groups (for example, on LinkedIn) where you can find people who have specific roles, such as sales reps, radiologists, designers, etc. Once you find the people you would like to interview, you can contact them directly or post a survey to the group.
-
Small offline meetups
Visit meetup.com, a website where users join groups around their interest and meet at offline events. If you are targeting healthcare practitioners, look for a meetup for healthcare professionals. You can contact both organizers and specific people within the group.
Read our blog post “Business Development Relationship Ladder: How to Build a Close Connection With Your Client.”
image source: Meetup
Step 4: Find the value proposition for your product ideas
Explain the value proposition for your product or service (e.g., what potential customers would receive from using your product/service). How do you like the example from Uber?
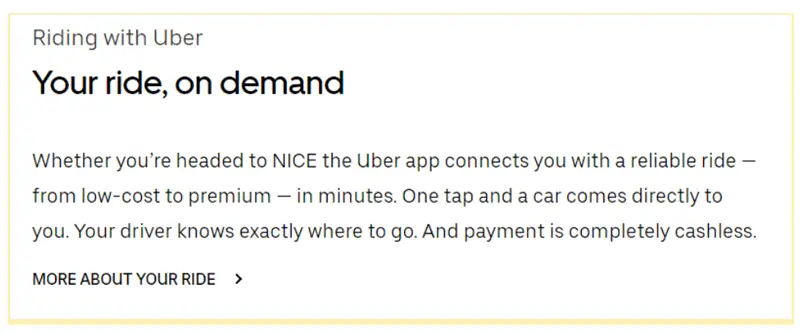
image source: Uber
Step 5: Launch an idea validation landing page
Landing pages might be extremely effective in the process of product validation. But before we get into the tools to use, we want to explain that there is a difference between users who SAY that they will buy your product and those that WILL buy. We will discuss both a traditional “coming soon” page and something a little better.
The “coming soon” case: Joey created a landing page giving the visitors a few lines about the product. He also asked for their email addresses to notify them when the product is released. In a matter of days, Joey has got 300 potential users. Wow!
You might be surprised to find out that he ended up with 10. The problem with these “coming soon” pages is that although collecting email addresses proves some interest in Joey’s idea, it doesn’t prove that those potential users are ready to pay for his product.
The “existing product” case: Joey's friend Ross decided to build a landing page that made it look like the product already existed. He even included a few plans and pricing. This way, he received email addresses only from those people who were ready to pay for his product. Instead of just collecting a bunch of email addresses, Ross spent time engaging in a dialogue with people who were willing to buy his product.
Now, let’s take a look at some tools you can benefit from when building your idea validation landing page.
Tools to use
-
Landing page builder
Use landing page creators such as Unbounce, Wishpond, etc.
-
Google Analytics
Connect your landing page to Analytics to dig deeper into the visitors’ experience. With the help of this tool, you’ll understand where the users are coming from, at what step they quit, and why.
-
Subscription form
Landing page builders often come with signup forms. However, you can also use something like Sumo or any other tools you like.

-
Connect to email marketing software
Keep in touch with your potential customers using MailChimp, SendGrid, SendPulse, and other email marketing services. Use email signature generator to make your email look more professional.
Step 6: Run customer validation survey
Polls and surveys are great tools for business idea validation. Pitch your ideas and see who likes them.
Tools to use
-
Google Forms
You can start with a simple survey of potential customers created in Google Forms. It can also be sent to friends and family, but keep in mind that they may not always be as objective as possible, so ask them to answer questions honestly, even if they don’t like something about your idea.
You can share a link to your Google Form in social networks as well. Place surveys not only on your page but also in groups and public places where your audience spends time.
Survey Anyplace
If you are looking for an intuitive tool with a wide range of design and branding opportunities, Survey Anyplace is perfect to collect feedback, validate your ideas or discover market opportunities. All surveys and polls can easily be shared on social media.
-
SurveyMonkey
For more accurate feedback, you can use the SurveyMonkey service. The platform helps to compile surveys to study the market. Here you can also test advertising campaigns, brand awareness, and naming.
Step 7: Paying customers are the best idea validation
If you need to get the most accurate results, be sure to measure the right metrics (check how many people are willing to pay). Consider building a landing page where visitors enter credit card information, and up until they click “Check out,” it all looks real. After that, you could show a message saying that the product will be released soon.
Step 8: Run Adwords campaign and FB ads to drive traffic
To understand the potential conversion, set up Facebook Ads/Google Adwords campaigns and drive traffic to your landing page. Feel free to check out our Facebook Ads Starter Guide: Key Aspects to Launch Your First Campaign.

image source: Semrush
Step 9: Crowdfunding as a way to validate a product idea
Crowdfunding is a way to collect money. It can also be used to test your idea. Offer people to finance a product that doesn't exist in exchange for its first copies. If the required amount is not collected, you will give the funds back to each donor. In this case, you will understand that the audience doesn’t need your product.
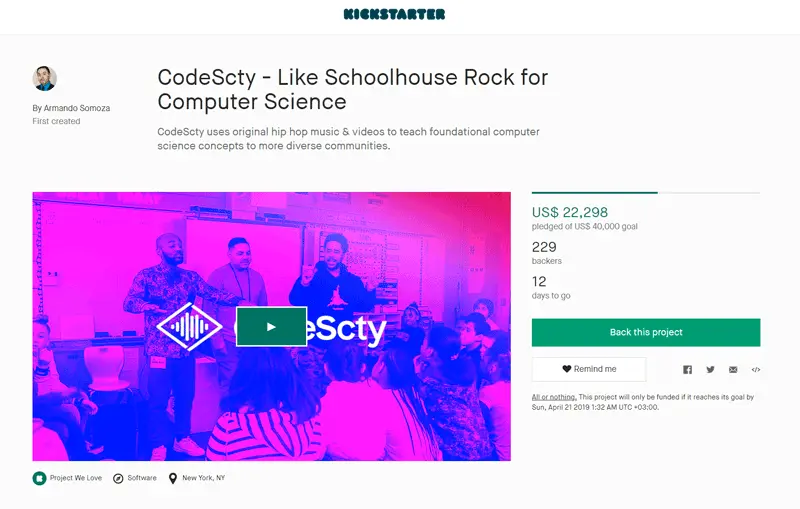
image source: kickstarter
Step 10: Build an MVP
If there were a book about the most crushing failures of startups, then it would have at least a thousand pages. Everyone makes strategic mistakes, even giants like Amazon. In 2014, the company announced a loss of $ 170 million after a failure with the Fire Phone. The reason for the failure is simple: no one needed this phone except for Amazon itself. The gadget was designed to connect users directly to the trading platform. Users have already used iPhone and Android smartphones to connect to Amazon. The lack of research analyzing user needs played a cruel joke with Amazon.
If you want to achieve success, you need to be sure that the product you are going to offer is exactly what users need. Developing a minimum viable product (MVP) can help you with this.
MVP meaning
MVP is the earliest version of the product which has only the necessary functions sufficient to convey fundamental values to the audience and test them on the first users. In general, MVP is aimed at gathering feedback and finding out whether users need a product at all. Early users can share their vision of functionality, which will allow developers to make adjustments to the product and plan future updates based on the data obtained about user preferences.
The MVP strategy reduces development costs and the risks of financial failure as a result of supplying an undesirable product to the market.
There are a lot of different approaches to creating an MVP. Today, we will be taking a look at only a few of them.
#1 The Wizard of Oz approach
Just as the Wizard of Oz pretended to be great and powerful, startuppers do the entire job manually instead of using any software. Another example is a founder of Zappos who had no shoes and no warehouse at first. To test his idea, he uploaded several photos of shoes, and once people ordered the shoes, he went to the shop, bought the needed pair, and shipped it to customers.
#2 Concierge approach
It is similar to the Wizard of Oz approach, but in this case, customers know that there are some people behind a provided service. This approach is aimed at communicating with potential customers and generating new ideas about the future product or service.
#3 A single-feature product approach
This one is pretty self-explanatory. Entrepreneurs launch a product with a minimum amount of features or just the one core feature.
Step 11: Participate in conferences with StartUp Alleys
Do you want to test your idea and get feedback from people all over the world? Go to a conference within your target industry and talk about your idea. This way you will understand if your product or service solves someone's problem. What’s more, perhaps you will find your first customers/testers there, who could even recommend you to their friends and colleagues.

image source: robinhood10
Analyze the data
So, we have gone through all validation steps: we generated some ideas (hypothesis), did research (action), collected results (data), and now it's time to analyze everything (insights). At this point, you should identify if your initial hypotheses were right, wrong, or still unclear. You might find out that it’s better to continue testing, to reshape your idea, to pivot, to create entirely new hypotheses, or even prove with evidence that your idea will bring success.
When to stop?
Finally, don't let validation turn into procrastination. As soon as you made sure that there was a market for your product or service, and people were willing to pay you, reach out to testers/early adopters and get enough feedback from them. When you come to the final product that passes the users’ control, you can say that you have a validated business idea.
Conclusion
To sum it up, let’s briefly walk through all the validation steps again.
- Write down the problem hypothesis;
- Research your competitors;
- Use Google Trends;
- Share your idea with relevant people;
- Find the value proposition for your product ideas;
- Launch a landing page;
- Run customer validation surveys;
- Understand the difference between those who want your product and those who pay for it;
- Take benefit of Google Adwords and Facebook Ads to drive traffic to your landing page;
- Consider crowdfunding as a way to validate a product idea;
- Build a minimum viable product (MVP);
- Participate in conferences.
By following these validation steps, you will be able to learn more about your customers, their problems, and their needs. When done properly, idea validation reduces the risks of wasting your time and money. So go ahead and test your idea. We believe your awesome product will see the world soon. Good luck.
We'd be happy if you would share this article in your social networks. Thank you!



